
What causes plantar fasciitis?
Peer reviewed by Dr Krishna Vakharia, MRCGPLast updated by Dr Doug McKechnie, MRCGPLast updated 30 Mar 2023
Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain in the bottom of your foot, usually around the heel and arch of the foot. It's caused by irritation and damage to the plantar fascia, a band of connective tissue that connects the heel bone to the base of the toes.
In this article:
Plantar fasciitis is caused by repeated injuries to the plantar fascia, causing lots of tiny tears in the fascia to develop. Things that put extra strain on the feet, and therefore the plantar fascia, can cause plantar fasciitis to occur - such as running, being overweight, or standing or walking for long periods of time. Tight calf muscles, high arches, or flat feet can put extra stress on the plantar fascia as well.
If you think you may have plantar fasciitis find out what to do here. This will tell you if you need to see a doctor and how it is treated.
In this series of articles centred around plantar fasciitis you can read about symptoms of plantar fasciitis, treatment for plantar fasciitis and the causes of plantar fasciitis - all written by one of our expert GPs.
The rest of this feature will take an in-depth look at the causes of plantar fasciitis as, at Patient, we know our readers sometimes want to have a deep dive into certain topics.
Continue reading below
What causes plantar fasciitis?
Plantar fasciitis is caused by repeated strain and injury to the plantar fascia. The plantar fascia acts like a shock absorber in the foot, helping to support the shape of the foot every time it hits the floor when running or walking, and also helping the foot bounce back when lifting it off the floor. When the plantar fascia is put under extra strain repeatedly, tiny tears can develop in the fascia, causing the symptoms of plantar fasciitis.
Plantar fasciitis position in foot
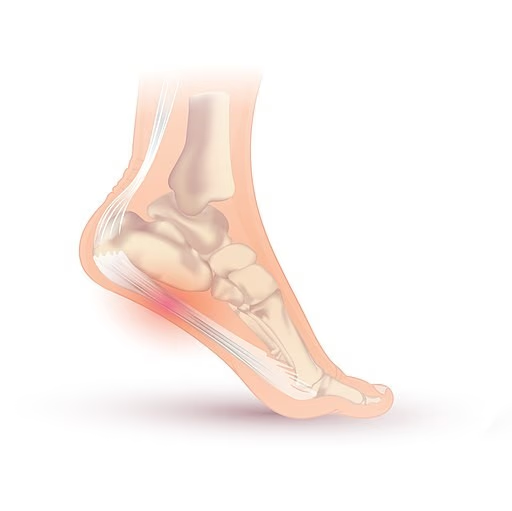
By Injurymap, CC BY 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Plantar fasciitis has lots of different causes and in many people, there is more than one reason for it to develop. Its can be difficult to find any one specific cause in some people.
Running, walking and standing
Plantar fasciitis is a common injury in runners. It also affects people who do lots of walking, or who are on their feet a lot - for example, because of their job. It's more likely to happen in people who have just started doing a lot more running, walking, or standing, and their body hasn't yet adjusted. All these things can put extra repeated stress on the plantar fascia and cause injury.
Hard surfaces
Running, walking, or standing on hard surfaces for long periods of time can put extra strain on the plantar fascia.
Overweight, obesity, and pregnancy
Carrying additional weight puts more strain on the feet and the plantar fascia whilst walking, standing and running.
Age-related changes
Plantar fasciitis can occur at any age, but is most common in people between the ages of 40 and 60. It's thought that this might be due to age-related changes in the plantar fascia, other parts of the feet, and the calf muscles.
Footwear
Some types of shoes put extra stress on the plantar fascia when walking, running or standing - such as flat shoes without any arch support or shoes without cushioning around the heel.
Tight muscles
Tight calf muscles are common in people with plantar fasciitis. Tense calf muscles can stop the ankle moving normally when walking, putting extra stress on the plantar fascia. Tight muscles in the hamstrings and feet can also cause this.
Walking patterns
Some people have a walking or running pattern that puts too much strain on the plantar fascia - such as overpronation, where the foot rolls inwards more than usual.
Different foot shapes
Having flat feet (pes planus) or the opposite, a high arch (pes cavus), can put extra stress on the plantar fascia.
Inflammatory joint problems
Although rare, there are some joint problems caused by inflammation and autoimmune issues that can cause plantar fasciitis. People with these conditions have other joint problems, not just plantar fasciitis.
These inflammatory conditions include ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, arthritis associated with inflammatory bowel disease, and reactive arthritis. People with these conditions can get inflammation at the point where tendons or ligaments connect to a bone - such as where the plantar fascia connects to the heel bone.
Patient picks for Heel and foot pain
How common is plantar fasciitis?
Plantar fasciitis is a very common cause of heel pain. It's estimated that around 4-7% of people have it, and that 8-10% of regular runners get plantar fasciitis.
Continue reading below
What causes plantar fasciitis to flare up?
Anything that puts extra stress and strain on the plantar fascia and soles of the feet can cause plantar fasciitis to flare up. For example, starting a new exercise regime, increasing the intensity of exercise, walking barefoot, or wearing shoes that don't give enough support to the foot can stress the plantar fascia and cause injury.
How to prevent plantar fasciitis
Avoiding the causes of plantar fasciitis can help to reduce the risk of it occurring or returning. This can also help treat plantar fasciitis. For example:
Maintaining a healthy weight - such as losing weight if living with obesity or overweight.
Wearing shoes that support the arch of the foot.
Building up gradually if starting a new exercise regime, or increasing the intensity of exercise.
Stretching your calf - especially the Achilles tendon - regularly.
Warming up before doing exercise.
Switching to different exercises whilst recovering - if a certain type of exercise causes the plantar fasciitis to flare up.
Running on soft surfaces, if possible.
Sometimes, a physical therapist can give advice on exercises and running technique to help reduce the risk of plantar fasciitis coming back.
Night splints might help people who suffer frequently with plantar fasciitis.
Article History
The information on this page is written and peer reviewed by qualified clinicians.
30 Mar 2023 | Latest version
30 Mar 2023 | Originally published
Authored by:
Dr Doug McKechnie, MRCGP

Feeling unwell?
Assess your symptoms online for free

