Plantar fasciitis
Heel and foot pain
Peer reviewed by Dr Toni Hazell, MRCGPLast updated by Dr Surangi Mendis, MRCGPLast updated 5 Jun 2024
Meets Patient’s editorial guidelines
- DownloadDownload
- Share
- Language
- Discussion
- Audio Version
In this series:Achilles tendinopathyAchilles tendon ruptureMetatarsalgiaMetatarsal fracturesMorton's neuromaFlat feet and fallen arches
Heel and foot pain are very common. A common cause is plantar fasciitis which causes pain under the heel. It usually goes away with time but various treatments may help.
In this article:
Video picks for Heel and foot pain
Continue reading below
What is plantar fasciitis?
Plantar fasciitis means inflammation of your plantar fascia. The plantar fascia is a band of tissue that connects your heel bone to the base of your toes.
It is a condition that affects around one in ten people at some point in their lives. It's also known as 'jogger's heel' - although you don't have to be a runner to develop it. Luckily, it usually gets better in time, but treatment may speed up your recovery.
So, what can you do about it? Useful treatment includes rest, good footwear, heel pads, painkillers and exercises. A steroid injection or other treatments may be used in more severe cases.
What is the plantar fascia?
Your plantar fascia is a strong band of tissue (like a ligament) that stretches from your heel (calcaneum) to your middle foot bones. It supports the arch of your foot and also acts as a shock absorber in your foot.
What causes plantar fasciitis?
Back to contentsRepeated small injuries to the fascia (with or without inflammation) are thought to be the cause of plantar fasciitis. The injury is usually near to where the plantar fascia attaches to your heel bone.
What makes it likely for someone to develop plantar fasciitis?
You are more likely to injure your plantar fascia in certain situations. For example:
If you are on your feet for a lot of the time, or if you do lots of walking, running, standing, etc, when you are not used to it or have previously had a more sedentary lifestyle.
If you have recently started exercising on a different surface - for example, running on the road instead of a track.
If you have been wearing shoes with poor cushioning or poor arch support.
If you are overweight - this will put extra strain on your heel.
If there is overuse or sudden stretching of your sole. For example - athletes who increase running intensity or distance; poor technique starting 'off the blocks', etc.
If you have a tight Achilles tendon (the big tendon at the bottom of your calf muscles above your heel). This can affect your ability to flex your foot and ankle and may make you more likely to damage your plantar fascia.
Plantar fasciitis may be confused with 'policeman's heel' but they are different. Policeman's heel is called plantar calcaneal bursitis - inflammation of the sack of fluid (bursa) under the heel bone (calcaneum). This is not as common as plantar fasciitis.
Often there is no apparent cause for plantar fasciitis, particularly in older people. A common wrong belief is that the pain is due to a bony growth, or 'spur', coming from the heel bone. Many people have a bony heel spur but not everyone with this develops plantar fasciitis.
Continue reading below
How common is plantar fasciitis?
Back to contentsPlantar fasciitis is common. Around 4-7% of people will develop plantar fasciitis at some time in their lives and it accounts for 11-15% of all foot problems that require professional treatment.
It is most common in people between the ages of 40 to 60 years. However, it can occur at any age. It is slightly more common in women than in men. It is also common in athletes.
Plantar fasciitis symptoms
Back to contentsPain is one of the main symptoms of plantar fasciitis. The inflamed plantar fascia can hurt when you put pressure on the foot while walking. This pain can be anywhere on the underside of your heel. However, commonly, one spot is found as the main source of pain. This is often about 4 cm forward from your heel and may be tender to touch.
The pain is often worst when you take your first steps on getting up in the morning, or after long-term rest where no weight is placed on your foot. Often, it's described as a stabbing or aching pain. Gentle exercise may ease things a little as the day goes by.
However, a long walk or being on your feet for long periods often makes the pain worse. Resting your foot usually eases the pain - this can be very frustrating for people who are trying to improve their fitness levels by taking up running!
Sudden stretching of the bottom of your foot may make the pain worse - for example, walking up stairs or on tiptoes. You may limp because of pain. Some people have plantar fasciitis in both feet at the same time.
Continue reading below
The anatomy of your foot
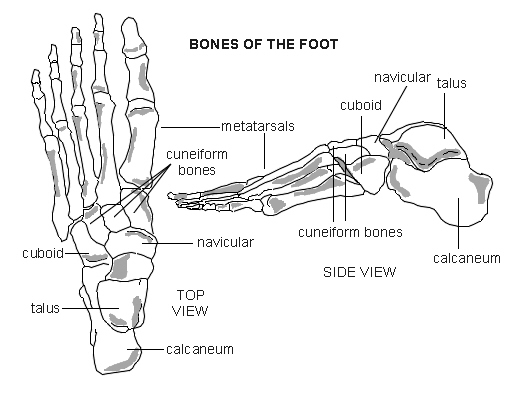
Back to contentsSpare a thought for your feet - they have to bear the weight of your whole body. There are many bones in each foot (see the images below) and these can briefly be divided into three parts:
Forefoot: made up of the toes (phalanges) and the five long bones (metatarsals). These are named from first to fifth. The first metatarsal bone is the largest and is the bone that joins to your big toe. Each toe has three phalanges, except the big toe which has only two. This means there are three joints in the toes (two in the big toe).
Midfoot: a collection of bones forming the arches of the foot.
Hindfoot: the ankle joint and the tarsal bones, including the biggest, the heel bone (calcaneum).
Heel and foot bones
What is the Achilles tendon?
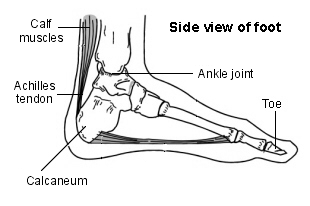
Your Achilles tendon is an important part of your leg. It is found just behind and above your heel. It joins your heel bone (calcaneum) to your calf muscles. The function of your Achilles tendon is to help in bending your foot downwards at the ankle, as you do when you're pointing your toes. (This movement is called plantar flexion.)
Foot and heel pain - Achilles tendon
There are also many other tendons, as well as muscles and ligaments, within your foot. The bones, ligaments and tendons within your foot form the foot arches. These arches are called the longitudinal and transverse arches. It is your foot arches that allow your foot to hold up the weight of your body. Nerves provide sensation to the skin of your foot.
What causes foot pain?
Where is the plantar fascia?
Heel diagram of plantar fascia
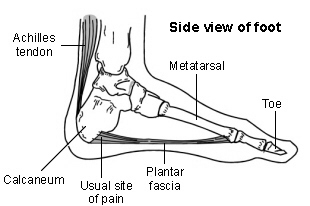
This diagram shows the position of the plantar fascia in relation to the bones in the foot. Inflammation of this band of tissue is where the pain associated with plantar fasciitis comes from - '-itis' is the medical term for inflammation.
What else can cause heel pain?
Back to contentsWhat is heel pain?
While plantar fasciitis is one of the most common causes of foot and heel pain, it is not the only reason:
Common causes of heel and foot pain
Plantar fasciitis (see below).
Inflammation of the Achilles tendon (Achilles tendinopathy) can cause pain in the back of the ankle, going down to the back of the heel.
Rupture of the Achilles tendon can cause sudden heel pain and problems walking.
In the ball of your foot:
Inflammation around the head of the metatarsal bones can cause pain in the forefoot.
So can Morton's neuroma, a problem with one of the nerves that run between the metatarsal bones.
Flat feet by contrast can cause pain almost anywhere in the foot, although usually the condition doesn't cause any symptoms.
Sever's disease is a painful inflammation of the heel that can affect children between the ages of 8 and 14 years.
There are also many conditions that can cause problems elsewhere in the body, as well as in the feet - for example:
Conditions that cause painful joints, such as:
Gout often causes sudden severe pain in the foot, typically the big toe.
Bunions (hallux valgus) also cause pain in the big toe but this comes on very gradually.
Problems with the nerves to the feet, such as peripheral neuropathy, sciatica or tarsal tunnel syndrome.
Problems with the blood vessels to the feet, which is usually due to peripheral arterial disease or diabetes.
How is plantar fasciitis diagnosed?
Back to contentsYour doctor can usually diagnose plantar fasciitis just by talking to you and examining your feet. Rarely, tests are needed if the diagnosis is uncertain or to rule out other possible causes of heel pain.
These can include X-rays of the heel (usually done to rule out other causes of pain rather than to diagnose plantar fasciitis) or an ultrasound scan of the fascia. An ultrasound scan usually shows thickening and swelling of the fascia in plantar fasciitis.
How long does plantar fasciitis take to heal?
Back to contentsPlantar fasciitis typically lasts between 6 to 12 months with the aid of the treatments like stretching exercises, which are covered below.
How to ease plantar fasciitis
Back to contentsUsually, the pain will ease in time. 'Fascia' tissue, like 'ligament' tissue, heals quite slowly. It may take several months or more to go. However, there is a variety of treatments that may help to speed recovery. A combination of different treatments may help. These vary from rest and simple exercises (most common) to surgery (rare).
Collectively, these initial treatments are known as 'conservative' treatments for plantar fasciitis:
Rest your foot
This should be done as much as possible. Avoid running, excess walking or standing, and undue stretching of your sole. Gentle walking and exercises described below are encouraged.
Footwear
Do not walk barefoot on hard surfaces. Choose shoes with cushioned heels and good arch support. A laced sports shoe rather than an open sandal is probably best. Avoid old or worn shoes that may not give a good cushion to your heel.
Heel pads and arch supports
You can buy various pads and shoe inserts to cushion the heel and support the arch of your foot. These work best if you put them in your shoes at all times, particularly if you have quite a high arch. The aim is to raise your heel by about 1 cm.
If your heel is tender, cut a small hole in the heel pad at the site of the tender spot. This means that the tender part of your heel will not touch anything inside your shoe. Place the inserts/pads in both shoes, even if you only have pain in one foot. A podiatrist may be able to help with specialist inserts like night splints.
Pain relief
Painkillers such as paracetamol will often ease the pain. Sometimes anti-inflammatory medicines such as ibuprofen are useful. These are painkillers but also reduce inflammation and may work better than ordinary painkillers. Some people find that rubbing a cream or gel that contains an anti-inflammatory medicine on to their heel is helpful.
An ice pack (such as a bag of frozen peas wrapped in a tea towel) held to your foot for 15-20 minutes may also help to relieve pain.
Exercises
Regular, gentle stretching of your Achilles tendon and plantar fascia may help to ease your symptoms. This is because most people with plantar fasciitis have a slight tightness of their Achilles tendon. If this is the case, it tends to pull at the back of your heel and has a knock-on effect of keeping your plantar fascia tight.
Also, when you are asleep overnight, your plantar fascia tends to tighten up (which is why it is usually most painful first thing in the morning). The aim of these exercises is to loosen up the tendons and fascia gently above and below your heel. Your doctor may refer you to a physiotherapist for exercise guidance.
Watch our physiotherapist taking you through all the exercises for plantar fasciitis in our video.
Exercises (done with or without shoes on) to help treat plantar fasciitis
Stand about 40 cm away from a wall and put both hands on the wall at shoulder height, feet slightly apart, with one foot in front of the other. Bend your front knee but keep your back knee straight and lean in towards the wall to stretch. You should feel your calf muscle tighten. Keep this position for several seconds, then relax. Do this about 10 times then switch to the other leg. Now repeat the same exercise for both legs but this time, bring your back foot forward slightly so that your back knee is also slightly bent. Lean against the wall as before, keep the position, relax and then repeat 10 times before switching to the other leg. Repeat this routine twice a day.
Stand on the bottom step of some stairs with your legs slightly apart and with your heels just off the end of the step. Hold the stair rails for support. Lower your heels, keeping your knees straight. Again you should feel the stretch in your calves. Keep the position for 20-60 seconds, then relax. Repeat six times. Try to do this exercise twice a day.
Sit on the floor with your legs out in front of you. Loop a towel around the ball of one of your feet. With your knee straight, pull your toes towards your nose. Hold the position for 30 seconds and repeat three times. Repeat the same exercise for the other foot. Try to do this once a day.
Sit on a chair with your knees bent at right angles and your feet and heels flat on the floor. Lift your foot upwards, keeping your heel on the floor. Hold the position for a few seconds and then relax. Repeat about 10 times. Try to do this exercise five to six times a day.
For this exercise you need an object such as a rolling pin or a drinks can. Whilst sitting in a chair, put the object under the arch of your foot. Roll the arch of your foot over the object in different directions. Perform this exercise for a few minutes for each foot at least twice a day. This exercise is best done without shoes on.
How is plantar fasciitis treated?
Back to contentsIf the above treatments are not helping to relieve your symptoms, or if you are someone such as an athlete who needs a quick recovery, other treatments are available. There is no one specific treatment for plantar fasciitis that appears to stand out as the best.
Steroid injections
A steroid (cortisone) injection is sometimes tried if your pain remains bad despite the above 'conservative' measures. It may relieve the pain in some people for several weeks but does not always cure the problem.
It is not always successful and may be sore to have done. Steroids work by reducing inflammation. Steroid injections do carry some risks, including (rarely) tearing (rupture) of the plantar fascia and for this reason they are less commonly done in the community these days - GPs will often refer to a service that can do the injection under ultrasound guidance.
Extracorporeal shock-wave therapy
In extracorporeal shock-wave therapy, a machine is used to deliver high-energy sound waves through your skin to the painful area on your foot. It is not known exactly how it works but it is thought that it might stimulate healing of your plantar fascia. One or more sessions of treatment may be needed.
This procedure appears to be safe but it is uncertain how well it works. This is mostly because of a lack of large, well-designed clinical trials. You should have a full discussion with your doctor about the potential benefits and risks.
In studies, most people who have had extracorporeal shock-wave therapy have little in the way of problems. However, possible problems that can occur include pain during treatment, skin reddening, and swelling of your foot or bruising.
Another theoretical problem could include the condition becoming worse because of rupture of your plantar fascia or damage to the tissues in your foot. More research into extracorporeal shock-wave therapy for plantar fasciitis is needed.
Other treatments for plantar fasciitis
Various studies and trials have been carried out looking at other possible treatments for plantar fasciitis. Such treatments include injection with botulinum toxin and treatment of the plantar fascia with radiotherapy. These treatments may not be widely available.
Some people benefit from wearing a special splint overnight to keep their Achilles tendon and plantar fascia slightly stretched. The aim is to prevent the plantar fascia from tightening up overnight. In very difficult cases, sometimes a plaster cast or a removable walking brace is put on the lower leg.
This provides rest, protection, cushioning and slight stretching of the plantar fascia and Achilles tendon. However, the evidence for the use of splint treatment of plantar fasciitis is limited.
Can you have surgery for plantar fasciitis?
Back to contentsThis may be considered in very difficult cases. Surgery is usually only advised if your pain has not eased after 12 months despite other treatments. The operation involves separating your plantar fascia from where it connects to the bone; this is called a plantar fascia release.
It may also involve removal of a spur on the heel bone (calcaneum) if one is present. Surgery is not always successful. It can cause complications in some people so it should be considered as a last resort. Complications may include infection, increased pain, injury to nearby nerves, or rupture of the plantar fascia.
What is the outlook (prognosis)?
Back to contentsMost people have completely recovered from an episode of plantar fasciitis within a year. However, some of the treatments described above may help to speed up your recovery.
How to prevent plantar fasciitis
Back to contentsThere are certain things that you can do to try to prevent plantar fasciitis, especially if you have had it before. These include:
Regularly changing training shoes used for running or walking.
Wearing shoes with good cushioning in the heels and good arch support.
Losing weight if you are overweight.
Regularly stretching of your calf, the plantar fascia and Achilles tendon, especially before exercise.
Avoiding exercising on hard surfaces.
Patient picks for Heel and foot pain

Foot care
Achilles tendon rupture
The Achilles tendon is at the back of the heel. It can be ruptured by sudden force on the foot or ankle. If your Achilles tendon is ruptured you will be unable to stand on tiptoe and will have a flat-footed walk. It is important to diagnose and treat this injury as soon as possible, to help promote healing. Treatment involves wearing a plaster cast or brace (orthosis) for several weeks, and possibly having an operation.
by Dr Doug McKechnie, MRCGP

Foot care
Achilles tendinopathy
Achilles tendinopathy is a condition that causes pain, swelling and stiffness of the Achilles tendon that joins the heel bone to the calf muscles. It is thought to be caused by repeated tiny injuries to the Achilles tendon. These may occur for a number of reasons, including overuse of the tendon - for example, in runners. Treatment includes rest, ice packs, painkillers and special exercises to help to stretch and strengthen the Achilles tendon. For most people, the symptoms of Achilles tendinopathy usually clear within 3-6 months of starting treatment.
by Dr Doug McKechnie, MRCGP
Further reading and references
- Extracorporeal shockwave therapy for refractory plantar fasciitis; NICE Interventional Procedures Guidance, August 2009
- Information and exercise sheet, plantar fasciitis; Versus Arthritis
Continue reading below
Article history
The information on this page is written and peer reviewed by qualified clinicians.
Next review due: 4 Jun 2027
5 Jun 2024 | Latest version

Ask, share, connect.
Browse discussions, ask questions, and share experiences across hundreds of health topics.

Feeling unwell?
Assess your symptoms online for free
Sign up to the Patient newsletter
Your weekly dose of clear, trustworthy health advice - written to help you feel informed, confident and in control.
By subscribing you accept our Privacy Policy. You can unsubscribe at any time. We never sell your data.