Gynaecological cancer
Peer reviewed by Dr Toni Hazell, MRCGPLast updated by Dr Philippa Vincent, MRCGPLast updated 26 May 2025
Meets Patient’s editorial guidelines
- DownloadDownload
- Share
- Language
- Discussion
- Audio Version
In this series:Cancer of the uterusOvarian cancerCervical cancerVulval cancerVulval intraepithelial neoplasiaCervical screening
A number of cancers can arise in the female reproductive organs. This leaflet explains where these organs are and links to information about the individual cancers.
In this article:
Video picks for Gynaecological cancer
Continue reading below
The female anatomy
Gynaecological cancers are those which arise in the female reproductive organs. So it helps to be able to picture what and where these are.
Female reproductive organs
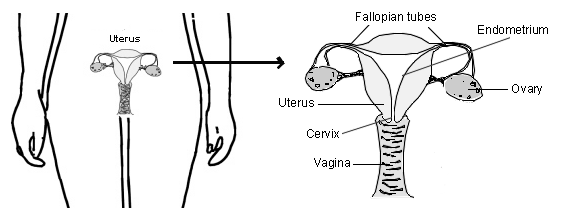
The womb (uterus) is a hollow organ with walls made of muscle. It is where the baby grows when you are pregnant. The inside lining of the womb is called the endometrium. This lining is shed every month causing periods (bleeding) when you are not pregnant.
The lower opening, or neck, of the womb is called the cervix. This is the opening through which the blood travels from the womb during a period. It stretches during childbirth.
The cervix sits at the top of a muscular tube called the vagina. This is the passage through which the blood passes during a period; this also stretches during childbirth. During sexual intercourse, when a penis is in the vagina, sperm is released from the penis and can enter the cervix into the womb. If there is an egg there, it can lead to a pregnancy.
The ovaries are two oval-shaped organs connected to the upper part of the womb on either side by the Fallopian tubes. Ovaries produce eggs and release them (where they are passed through the Fallopian tubes to the womb) in a monthly process called ovulation. The ovaries also produce the female hormones, oestrogen and progesterone.
The vulva is the part of the female reproductive system which is on the outside. It is the part of the genital area which surrounds the opening of the vagina.
Female Genitals
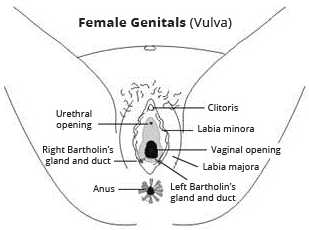
The vulva includes:
The labia majora. These are, in effect, large folds of skin.
The labia minora. These are more delicate folds of skin just inside the labia majora.
The clitoris - a small organ involved with sexual arousal.
Tiny glands, the most prominent being the Bartholin's glands.
The entrance to the urethra - the tube through which urine is passed from the bladder.
The entrance to the vagina.
What is cancer?
Back to contentsCancer is a condition where cells of a particular body organ multiply out of control. These abnormal cells can then spread around the body, causing damage and harm. Cancers in different organs are different illnesses, with different symptoms and different treatments. See the separate leaflet called Cancer.
Playlist: Gynae Cancer Q&A
5 videos
What is vaginal cancer?
Prof Lesley Regan, FRCOG
What is vaginal cancer?
Prof. Lesley Regan, FRCOG

Do gynae cancers cause bleeding?
Dr. Sarah Jarvis MBE, FRCGP

What are the symptoms of gynae cancer?
Dr. Sarah Jarvis MBE, FRCGP

Are gynae cancers painful?
Dr. Sarah Jarvis MBE, FRCGP

Can gynae cancers cause infertility?
Dr. Sarah Jarvis MBE, FRCGP
Continue reading below
What types of gynaecological cancers are there?
Back to contentsCancer can arise in any of the female reproductive organs. Click on the links below to read about each individual type of cancer.
Cancer of the vulva. A pre-cancerous skin condition called vulval intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN) can, in some cases, turn into cancer of the vulva if not treated.
Cancer of the vagina. This is very rare. It tends to occur in older women.
Cancer of the Fallopian tubes. This is rare. It tends to have similar symptoms to ovarian cancer and is diagnosed and treated in much the same way.
Is there screening for gynaecological cancers?
Back to contentsCurrently in the UK there is a national screening programme for cervical cancer, but none of the other gynaecological cancers. This is because cervical cancer, in many cases, can be picked up in the very early stages, before it is even cancer. Typical cell changes are picked up in a smear test. Read about cervical screening (the cervical smear test) for more information. This pre-cancer stage can be treated so that cancer doesn't develop. This is done during a process called colposcopy. Read about colposcopy and cervical treatments.
Studies have been done to look into whether ovarian cancer screening might be possible in the future. The biggest study, looking at scans and blood tests, ended in 2024 and did not show any reduction in deaths from ovarian cancer. Therefore, screening for ovarian cancer is not likely to become available in the near future.
Patient picks for Gynaecological cancer

Cancer
Cancer of the uterus
Uterine cancer is a cancer which starts in the lining of the uterus (womb). The most common type of uterine cancer is endometrial cancer.
by Dr Hayley Willacy, FRCGP

Cancer
Ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer is the sixth most common cancer in women in the UK. It is more common than cancer of the neck of the womb (cervical cancer).
by Dr Hayley Willacy, FRCGP
Further reading and references
- Ovarian cancer - the recognition and initial management of ovarian cancer; NICE Clinical Guideline (April 2011 - last updated October 2023)
- Endometrial cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up; European Society for Medical Oncology (2016)
- Newly diagnosed and relapsed epithelial ovarian carcinoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up; European Society for Medical Oncology (2013 - last updated 2020)
- Ovarian cancer statistics; Cancer Research UK
Continue reading below
Article history
The information on this page is written and peer reviewed by qualified clinicians.
Next review due: 25 May 2028
26 May 2025 | Latest version
28 Nov 2017 | Originally published

Ask, share, connect.
Browse discussions, ask questions, and share experiences across hundreds of health topics.

Feeling unwell?
Assess your symptoms online for free
Sign up to the Patient newsletter
Your weekly dose of clear, trustworthy health advice - written to help you feel informed, confident and in control.
By subscribing you accept our Privacy Policy. You can unsubscribe at any time. We never sell your data.