Thyroid lumps
Including goitre
Peer reviewed by Dr Hayley Willacy, FRCGP Last updated by Dr Colin Tidy, MRCGPLast updated 12 Aug 2024
Meets Patient’s editorial guidelines
- DownloadDownload
- Share
- Language
- Discussion
- Audio Version
Medical Professionals
Professional Reference articles are designed for health professionals to use. They are written by UK doctors and based on research evidence, UK and European Guidelines. You may find the Neck lumps and bumps article more useful, or one of our other health articles.
In this article:
Continue reading below
What are thyroid lumps?
Most thyroid lumps are benign but around 5% are malignant and it is important to distinguish this sinister minority.1
The term goitre refers to enlargement of the thyroid gland. A thyroid nodule may be a lump in an otherwise normal thyroid gland. However, goitres may consist of many nodules (multinodular goitre) and solitary nodules may exist within a goitre. Nodules may be cystic, colloid, hyperplastic, adenomatous or cancerous.
Iodine deficiency is the most common cause of goitre worldwide, but not common in the UK.2 In countries where iodine is added to salt, autoimmune conditions (Hashimoto's thyroiditis and Graves' disease) are more common causes. Medication (such as lithium and amiodarone) may cause thyroid enlargement. It may also occur in pregnancy and menopause.
See also the separate articles Thyroid cancer and Neck lumps and bumps.
How common are thyroid lumps? (Epidemiology)3
Back to contentsBetween 4-7% of adults have palpable thyroid lumps. Many more will be detectable on high-definition ultrasonography. Up to 40% of people having an ultrasound scan on their neck are found to have a thyroid nodule incidentally, and similar numbers are found incidentally at autopsy. 95% of these thyroid lumps in adults are benign.
Thyroid cancer represents 1% of all malignancies.
Thyroid nodules are uncommon in children and adolescents (1-1.5% are estimated to have palpable lumps). However, the risk of nodules being cancerous in this population is higher.4
Continue reading below
Risk factors56
Back to contentsGoitres and thyroid lumps are more common in areas of low iodine consumption. This is less likely in countries where iodine is added to table salt.
Conversely, excessive consumption of iodine (found in seaweed) can cause goitres.
Malignancy is more common where benign thyroid disease has existed.
The risk of malignancy in a thyroid nodule is higher under the age of 20 and over the age of 70.3
Thyroid nodules and cancers are more common after exposure to radiation. This includes therapeutic radiotherapy, and exposure to radiation following events such as those in Hiroshima and Chernobyl.
Smoking increases the risk of nodular goitre.
Family history.
Medication such as amiodarone and lithium.
There is some evidence that milk-alternative drinks pose a possible increased risk for iodine deficiency in the UK.7 This study examined the iodine content of 47 milk alternatives, including soya, almond, coconut, oat, rice, hazelnut, and hemp, and compared it with that of cows' milk. The majority of milk-alternative drinks did not have adequate levels of iodine, with concentrations found to be around 2% of that found in cows' milk. It is important that people who consume milk-alternative drinks realise that they will not be replacing the iodine from cows' milk which is the main UK source of iodine. This is particularly important for pregnant women and those planning a pregnancy.
Presentation
Back to contentsSymptoms
Thyroid lumps are often asymptomatic and are noticed by family members or seen in the mirror.
They may sometimes cause pain and rarely present with features of compression of the trachea.
Ask about previous radiation.
Signs
Ask the patient to drink some water and note the thyroid move as she/he swallows.
Note enlargement or asymmetry.
Stand behind a seated patient and use the second and third fingers of both hands to examine the gland as she/he swallows again.
Note lumps, asymmetry, size and tenderness.
Check for regional lymphadenopathy.
Struma
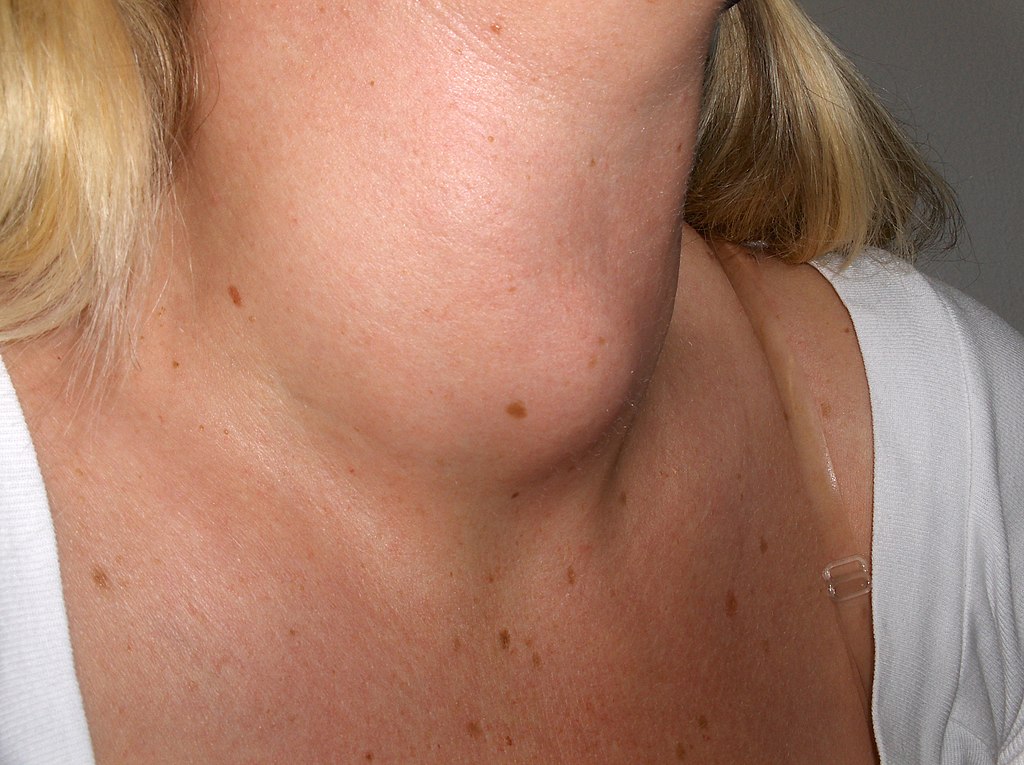
© Drahreg01, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Drahreg01, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Continue reading below
Referral8
Back to contentsEmergency hospital admission
If symptoms of upper airway obstruction, such as stridor.
Urgent referral
An unexplained thyroid lump.
A thyroid mass associated with unexplained hoarseness or voice change.
A thyroid mass associated with cervical lymphadenopathy or supraclavicular lymphadenopathy.
Sudden onset of a rapidly expanding painless thyroid mass, significantly increasing in size over days and weeks.
A suspected thyroid nodule with associated compressive symptoms, such as breathlessness or dysphagia.
Child with a thyroid nodule or goitre.
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommends: Consider a suspected cancer pathway referral for thyroid cancer in people with an unexplained thyroid lump. In a suspected cancer pathway referral, a person should receive a diagnosis or ruling out of cancer within 28 days of being referred urgently by their GP for suspected cancer.9
Non-urgent referral
Thyroid nodules with abnormal TFTs. Refer to an endocrinologist.
Sudden onset of pain within a thyroid lump. (Likely cause is a bleed into a thyroid cyst.)
A thyroid nodule picked up incidentally on an ultrasound scan, CT, or MRI, which is more than 1 cm in diameter, if there are no suspicious features of malignancy.
Suspicion of malignancy includes a known diagnosis or symptoms suspicious of local malignancy (eg, upper airway or upper gastrointestinal tract), or haematological malignancy (eg, leukaemia or lymphoma). Have a higher index of suspicion for malignancy if the person is 40 years of age or older.
Do not routinely arrange further investigations such as a neck ultrasound scan in primary care, as this may cause diagnostic delay.
Consider monitoring in primary care if there is:
An adult with a history of a longstanding unchanging thyroid nodule or mass over several years, with no palpable cervical lymphadenopathy and no other red flags or risk factors for malignancy.
A non-palpable, asymptomatic thyroid nodule picked up incidentally on an ultrasound scan, CT, or MRI, which is less than 1 cm in diameter, with no associated lymphadenopathy and no other red flags or risk factors for malignancy.
Differential diagnosis
Back to contentsThyroid lumps and swellings
Non-toxic (simple) goitre - non-functioning nodules. TFTs are normal.
Toxic multinodular goitre - functioning nodules. TFTs are abnormal.
Retrosternal goitre (usually multinodular).
Hyperplastic nodule (single nodule or part of multinodular goitre).
Colloid nodule.
Thyroid adenoma.
Thyroid cyst.
Graves' disease - diffusely enlarged overactive thyroid gland.
Hashimoto's thyroiditis - autoimmune destruction of the gland may cause diffuse enlargement.
Other types of thyroiditis:
De Quervain's thyroiditis - neck pain, fever and lethargy soon after an upper respiratory infection or a viral illness.
Acute suppurative thyroiditis - results from bacterial or fungal infection causing abscess.
Non-thyroid lumps and swellings
Congenital and developmental swellings:
Branchial cyst
Dermoid cyst
Laryngocele
Lymph nodes - swelling due to inflammation, infection or malignancy.
Salivary gland swellings - tumours, calculi, inflammation
Non-thyroid benign and malignant tumours - lipomas, fibromas, vascular tumours, sarcomas.
Diagnosing thyroid lumps (Investigations)
Back to contentsThyroid function tests
GPs are recommended to perform TFTs to determine the need for referral, and if so to whom.
Those with abnormal TFTs and no suspicious features should be referred to an endocrinologist.
Those with thyroid swelling and normal TFT should be referred under the timeline in the 'Red flag features' section above.
Those patients with a new thyroid swelling where cancer is suspected, GPs should refer under two-week wait rule.10 Referral should be to a surgeon, endocrinologist or other member of a specialist multidisciplinary team.
Ultrasound
This is highly sensitive for detection and characterisation of thyroid nodules11. It is far more sensitive than clinical examination and only a small percentage of nodules detected by ultrasound are clinically palpable. Ultrasound helps to inform which nodules need aspiration for cytology.
Fine-needle aspiration (FNA)
This provides tissue for cytology. It is performed under ultrasound guidance for maximum accuracy11. It is safe, inexpensive and provides direct information.
Basal plasma calcitonin and carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)
These are not used routinely but are measured if medullary thyroid cancer is suspected.
CT scans and MRI scans
These may be needed to detect local and mediastinal spread and regional lymph nodes if a neoplastic cause is identified.
Management of thyroid lumps
Back to contentsFurther reading and references
- Monitoring thyroid disease, Thyroid disease assessment and management; National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Nov 2019.
- Syrenicz A, Koziolek M, Ciechanowicz A, et al; New insights into the diagnosis of nodular goiter. Thyroid Res. 2014 Jun 17;7:6. doi: 10.1186/1756-6614-7-6. eCollection 2014.
- Ultrasound-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for benign thyroid nodules; NICE Interventional Procedure Guidance, June 2016
- Mehanna HM, Jain A, Morton RP, et al; Investigating the thyroid nodule. BMJ. 2009 Mar 13;338:b733. doi: 10.1136/bmj.b733.
- Carle A, Krejbjerg A, Laurberg P; Epidemiology of nodular goitre. Influence of iodine intake. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014 Aug;28(4):465-79. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2014.01.001. Epub 2014 Jan 10.
- Knox MA; Thyroid nodules. Am Fam Physician. 2013 Aug 1;88(3):193-6.
- Gupta A, Ly S, Castroneves LA, et al; A standardized assessment of thyroid nodules in children confirms higher cancer prevalence than in adults. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013 Aug;98(8):3238-45. doi: 10.1210/jc.2013-1796. Epub 2013 Jun 4.
- Knudsen N, Brix TH; Genetic and non-iodine-related factors in the aetiology of nodular goitre. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014 Aug;28(4):495-506. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2014.02.005. Epub 2014 Mar 6.
- De Luca F, Aversa T, Alessi L, et al; Thyroid nodules in childhood: indications for biopsy and surgery. Ital J Pediatr. 2014 May 19;40:48. doi: 10.1186/1824-7288-40-48.
- Bath SC, Hill S, Infante HG, et al; Iodine concentration of milk-alternative drinks available in the UK in comparison with cows' milk. Br J Nutr. 2017 Oct;118(7):525-532. doi: 10.1017/S0007114517002136. Epub 2017 Sep 26.
- Thyroid lump; NICE Clinical Knowledge Summary. October 2020.
- Suspected cancer: recognition and referral; NICE guideline (2015 - last updated January 2026)
- Neck lump; NICE CKS, October 2020 (UK access only)
- Thyroid disease: assessment and management; NICE guidance (November 2019 - last updated October 2023)
Continue reading below
Article history
The information on this page is written and peer reviewed by qualified clinicians.
Next review due: 11 Aug 2027
12 Aug 2024 | Latest version

Ask, share, connect.
Browse discussions, ask questions, and share experiences across hundreds of health topics.

Feeling unwell?
Assess your symptoms online for free