
Scarlet fever: a doctor's advice
Peer reviewed by Dr Colin Tidy, MRCGPLast updated by Dr Krishna Vakharia, MRCGPLast updated 14 Dec 2023
Meets Patient’s editorial guidelines
- DownloadDownload
- Share
- Language
- Discussion
- Audio Version
With a surge in cases of scarlet fever, GP and mum, Dr Krishna Vakharia, our clinical director here at Patient.info, talks about what you need to know and what to do if you're worried.
In this article:
Video picks for Skin rashes
When is a fever or sore throat more than just that and when does it become scarlet fever?
When our then 3-year-old developed a fever, was sick, and then felt better - we put it down to a bug. As this is our third child, we are used to dealing with kids with fevers, runny noses, and being sick.
A day later, he was off his food and had a high temperature. Looking into his mouth, I saw white spots on his tongue - a sign of scarlet fever. He had also developed a rash - another scarlet fever symptom.
As a GP, I knew the signs, so I rang 111, and a couple of hours later I had a prescription for antibiotics. Within 48 hours he was a lot better and starting to eat more. We later heard that there were a few children in his nursery that had been treated for scarlet fever.
Continue reading below
What is scarlet fever?
Bacteria called Group A streptococcus (GAS) - or strep A - can cause a number of different infections such as impetigo, cellulitis, and strep A throat (bacterial tonsillitis) These bacteria can also cause scarlet fever. This infection usually affects children under 10, but adults too - It is very infectious.
Scarlet fever has been around for centuries and every few years, there is a rise in cases. It was the main cause of death in children under 10 in the 1800s, due to people living in overcrowded houses. Now, as people are more spread out, the infection tends to be more contained so there are fewer deaths.
How common is scarlet fever?
Back to contentsIn the UK there are normally a few cases of scarlet fever every year - these tend to be in children and usually come with mild symptoms. Every few years, there is usually a period that is much worse than others. The last outbreak was in 2017-2018 when the highest number of cases since 1960 were recorded. We have also seen increased cases of unwell children with pneumonia or invasive Group A strep (iGAS) - causing more widespread infection.
iGAS is when Strep A goes into the blood stream or anywhere else it shouldn't, such as in the muscles or the lungs. It can make you very unwell and can lead to death. It is quite rare, but cases are increasing.
Continue reading below
What are the symptoms of strep A?
Back to contentsThe classic symptoms of strep A throat are the same as those of tonsillitis. GPs use the Centor criteria to decide when someone may need antibiotics. Two or more of these symptoms usually means that a sore throat is likely to be caused by strep A. This criteria is hard to use in children as they often have symptoms that may not fit. In these cases we do a thorough examination to see how likely it is their symptoms are due to strep A.
Strep A symptoms
Sore throat.
Fever - temperatures are usually over 38°C.
No cough.
White spots on the tonsils.
Painful, swollen neck lymph nodes.
It is often very difficult to predict when strep A throat can become scarlet fever.
How to tell if it's scarlet fever
My son had a sore throat with red and white spots on his tonsils first, and then I noticed he had a 'strawberry tongue' - a red tongue covered in white spots. On his tummy, he had developed a red, bumpy rash that felt like sandpaper.
Strawberry tongue
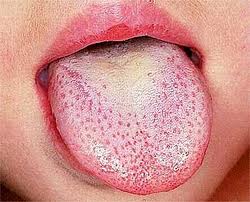
In people with darker skin, the rash is often difficult to see so doctors usually go by feel. This rash can spread throughout the body and can make the skin peel.
In most cases, antibiotics will make patients better. All that's needed to prevent spreading Strep A is to stay clear of others while you have the symptoms, and for 24 hours after you start antibiotics. The rash can last for up to seven days and often children can feel quite tired during the whole episode.
You can go back to school or work once you have been on antibiotics for 24 hours and you no longer have a fever.
When should we worry?
Back to contentsCall your doctor or go to A&E immediately if you have these symptoms:
No improvement after 48 hours of antibiotics.
If temperatures don't go down after giving paracetamol and ibuprofen.
Fever lasting more than five days.
Symptoms are getting worse.
If children have stopped eating and drinking.
If there are less than three good wet nappies or children have not been for a wee, or have a dry nappy for more than 12 hours.
Call 999/emergency numbers if:
Your child is lethargic, unresponsive.
They have fever, headache and are not moving their neck.
The rash does not disappear with the glass test - when you place the side of a glass against the rash and it can still be seen.
They are not making sense when they talk.
Light is affecting their eyes.
They cannot swallow their saliva and are drooling.
They are struggling to breathe- if you can see the ribs being sucked in or they cannot talk or lie flat because they are too breathless.
What are the complications of scarlet fever?
As well as the increase in children with complications from scarlet fever, there has also been an increase in pneumonia and iGAS. Both can cause serious illness.
Practical tips for managing a sore throat
Ice lollies - they provide energy and fluids. They are also soothing when you have a burning throat.
Water - drink often and take sips. Try not to glug down too much at once as this can make you feel sick.
Food - just eat what you can and want to eat, same goes for kids. Even if, like in my child’s case, it is just yogurt and white chocolate buttons. They can catch up on nutrition when they feel better.
Take paracetamol and ibuprofen as they need it for fever and pain. Look at the packet for recommended doses and never give more than this.
If you are not sure, or you're worried - seek help.
As a parent, it can be hard to work out when to worry and call for help. I often tell my patients that you know your child the best, so if you are concerned, call your doctor.
Scarlet fever is still rare, and more often than not your child will have a sore throat from a virus. If it is strep A your child may need antibiotics. If there is a scarlet fever alert - often from the government or schools - it is really there to let GPs and parents know to explore further if confronted with a fever and sore throat - and to then act quickly when there may be a chance it could be scarlet fever or iGAS.
Patient picks for Skin rashes

Skin, nail and hair health
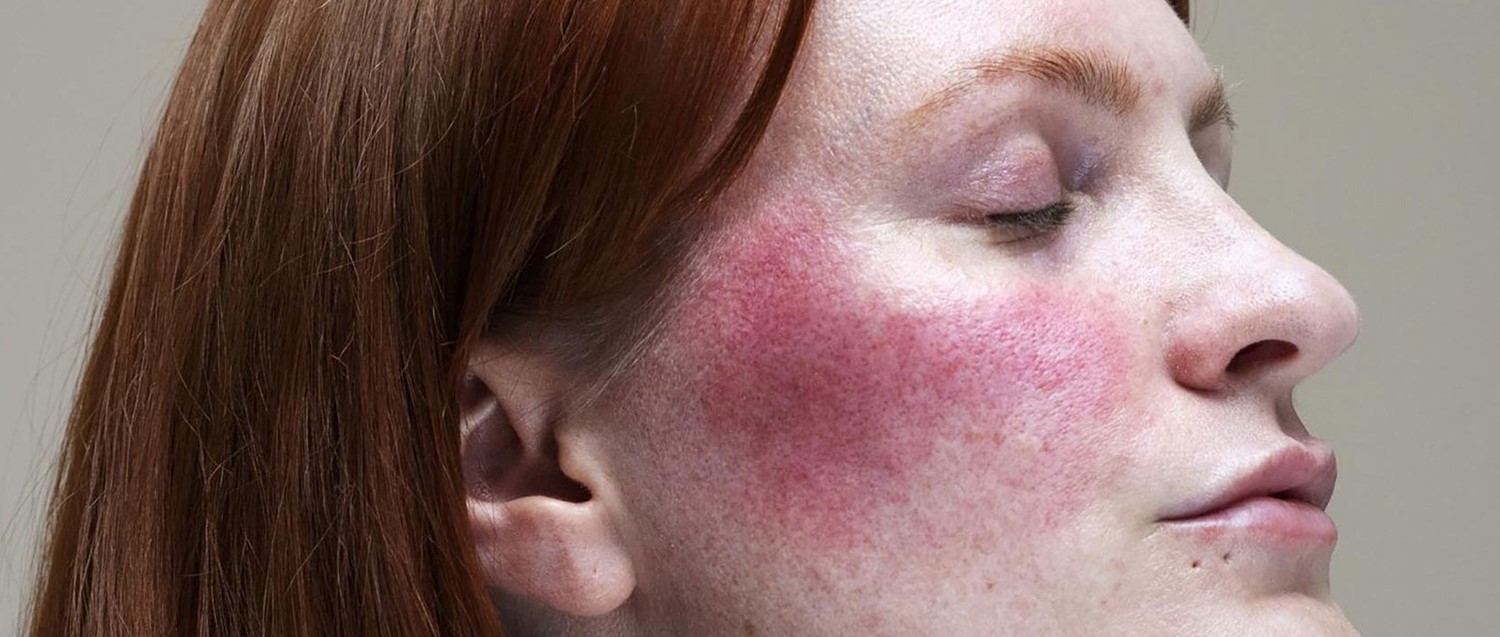
Common rosacea triggers and how to avoid them
One in ten people in the UK are thought to be suffering from rosacea - a condition that causes redness and flushing of the skin. Like many skin conditions, its exact cause is unknown. But the good news is that treatments are available, and people living with rosacea can take steps to minimise redness and flare-ups.
by Gillian Harvey
Skin, nail and hair health
Rosacea treatments: which is right for you?
Living with rosacea can be difficult. It can be a great source of stress and really impact your quality of life when you have to deal with any facial skin problems. Sadly, 10% of the population experience this skin condition, but the good news is that there are many treatment options. The right one for you will depend on which symptoms you have.
by Amberley Davis
Continue reading below
Article history
The information on this page is peer reviewed by qualified clinicians.
14 Dec 2023 | Latest version
5 Dec 2022 | Originally published
Authored by:
Dr Krishna Vakharia, MRCGP

Ask, share, connect.
Browse discussions, ask questions, and share experiences across hundreds of health topics.

Feeling unwell?
Assess your symptoms online for free
Sign up to the Patient newsletter
Your weekly dose of clear, trustworthy health advice - written to help you feel informed, confident and in control.
By subscribing you accept our Privacy Policy. You can unsubscribe at any time. We never sell your data.