CT scan
Preparation and complications
Peer reviewed by Dr Colin Tidy, MRCGPLast updated by Dr Rachel Hudson, MRCGPLast updated 20 Jun 2023
Meets Patient’s editorial guidelines
- DownloadDownload
- Share
- Language
- Discussion
- Audio Version
Note: the information below is a general guide only. The arrangements, and the way tests are performed, may vary between different hospitals. Always follow the instructions given by your doctor or local hospital.
In this article:
Video picks for Imaging
Continue reading below
What is a CT scan?
A CT scan is a specialised X-ray test. It can give quite clear pictures of the inside of your body. In particular, it can give good pictures of soft tissues of the body which do not show on ordinary X-ray pictures.
CT stands for computerised tomography. It is sometimes called a CAT scan. CAT stands for computerised axial tomography. (Sometimes the word 'computed' is used instead of 'computerised'.)
How is a CT scan done?
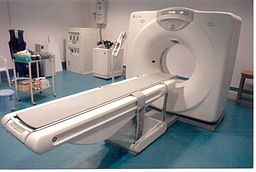
Back to contentsThe CT scanner looks like a giant thick ring. Within the wall of the scanner there is an X-ray source. Opposite the X-ray source, on the other side of the ring, are X-ray detectors.
You lie on a couch which slides into the centre of the ring until the part of the body to be scanned is within the ring.
The X-ray machine within the ring rotates around your body. As it rotates around, the X-ray machine emits thin beams of X-rays through your body, which are detected by the X-ray detectors.
CT scanner
© NithinRao (Own work) [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons
By NithinRao (Own work) [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons
The detectors detect the strength of the X-ray beam that has passed through your body. The more dense the tissue, the less X-rays pass through. The X-ray detectors feed this information into a computer.
Different types of tissue with different densities show up as a picture on the computer monitor, in different colours or shades of grey. So, in effect, a picture is created by the computer of a slice (cross-section) of a thin section of your body.
As the couch moves slowly through the ring, the X-ray beam passes through the next section of your body. So, several cross-sectional images of the part of your body being investigated are made by the computer.
Newer scanners can even produce 3-dimensional pictures from the data received from the various slices of the part of the body being scanned.
Continue reading below
What is a CT scan used for?
Back to contentsA CT scan can be done on any section of the head or body. It can give clear pictures of bones. It also gives clear pictures of soft tissues, which an ordinary X-ray test cannot show, such as muscles, organs, large blood vessels, the brain and nerves.
The most commonly performed CT scan is of the brain - to determine the cause of a stroke, or to assess serious head injuries. Other uses of a CT scan include:
To detect abnormalities in the body, such as tumours, abscesses, abnormal blood vessels, etc, when they are suspected by symptoms or other tests.
To give a surgeon a clear picture of an area of your body before certain types of surgery.
To pinpoint the exact site of tumours prior to radiotherapy.
To help doctors find the right place to take tissue samples (biopsies).
Preparing for a CT scan
Back to contentsUsually very little. It depends on which part of your body is to be scanned. You will be given instructions by the CT department appropriate for the scan to be done. These include:
Removing any metal objects from your body, such as jewellery, hair clips, etc.
Don't wear clothes with metal zips, studs, etc.
You may be asked not to eat or drink for a few hours before your scan.
Potentially stopping certain medicines before the procedure.
If you need an injection of contrast, as described below, it may be necessary to stop certain medicines before the procedure. This may apply to people taking metformin, a medicine used to treat diabetes. If you are taking this medication your doctor should give you instructions about what to do.
Further preparations
In some situations, depending on what part of the body is being scanned, one of the following may be needed. These aim to block a certain amount of X-ray going through various tissues. This helps to give better contrast between different organs and tissues on the scan pictures.
For abdominal and pelvic scans you may be asked to have a special drink before the scan. This helps to show up the stomach and bowel more clearly.
For pelvic scans, some fluid may be put into your back passage (rectum).
For pelvic scans, women may be asked to insert a tampon into the vagina.
Sometimes a dye (contrast agent) is injected into the bloodstream via a vein in your arm. The dye may give you a flushing feeling and an odd taste in your mouth, which soon goes.
What is a CT Scan with contrast?
Sometimes you will be given a colourless substance either as a drink, as an injection, or inserted into your rectum, which will show up on the CT scan images as white (as it blocks the x-rays). This is used to show more details of structures such as blood vessels and the intestine/bowel. Contrast often contains iodine, which some people may be allergic to - if you are allergic to iodine you should inform the scan department, however you will be asked about allergies before you have the scan. If you do suffer an allergic reaction to iodine following being given it for a CT this may cause itching, wheezing or feeling sick. This is usually short lived. Rarely, a delayed allergic reaction several hours after the scan can occur which causes an itchy rash - if you have a reaction following a CT scan with contrast you should contact A&E or your GP practice.
The contrast is got rid of from your body in your urine.
Editor’s note
Dr Krishna Vakharia, 1st November 2024
If you are having a scan with contrast it is also important to let the department know if you have kidney disease or have had a kidney transplant. Let them know if you are under a kidney specialist or a urologist. You may also be asked to stop certain medications such as some used for high blood pressure before a scan with contrast. Your doctor or scan department will discuss this with you if this is something you need to do.
Is a CT scan painful?
The CT scan itself is painless. You cannot see or feel X-rays. You will be asked to stay as still as possible, as otherwise the scan pictures may be blurred.
How long does a CT scan take?
Conventional CT scans can take between 5-30 minutes, depending on which part (or parts) of the body is being scanned. More modern CT scans (helical CT scans) take less than a minute and also use less radiation.
Continue reading below
Can anybody be with me during the CT scan?
Back to contentsBecause the scan uses X-rays, other people should not be in the same room. The operator controls the movement of the couch and scanner from behind a screen or in a separate control room. (This protects them from repeated exposure to X-rays.)
However, you can talk to them, usually via an intercom, and you will be observed at all times on a monitor. Some people feel a little anxious or claustrophobic in the scanner room when they are on their own. A mild sedative may be offered if you are particularly anxious.
What can I expect after the CT scan?
Back to contentsYou can return to your normal activities as soon as the scan is over. However, if you had a sedative for the scan, you will need someone to accompany you home. You will not be able to drive until the effect of the sedative wears off.
The pictures from the scan are studied by an X-ray doctor (radiologist) who sends a report to the doctor who requested the scan.
Are there any possible complications regarding a CT scan?
Back to contentsComplications are rare. As discussed above, some people have an allergic reaction to the dye (contrast agent) which is sometimes used. This is rare. It can be treated immediately. Very rarely, the dye may cause some kidney damage, most commonly in people already known to have kidney problems.
Pregnant women
If possible, pregnant women should not have a CT scan, as there is a small risk that X-rays may cause an abnormality to the unborn child.
Risks of X-ray radiation used in CT scans
CT scans use X-rays, which are a type of radiation. Exposure to large doses of radiation is linked to developing cancer or leukaemia - often many years later.
The dose of X-ray radiation needed for a CT scan is much more than for a single X-ray image but is still generally quite a low dose. The risk of harm from the dose of radiation used in CT scanning is thought to be very small but it is not totally without risk.
As a rule, the higher the dose of radiation, the greater the risk. So, for example, the larger the part of the body scanned, the greater the amount of radiation dose. And, repeat CT scans over time cause an overall increase of dose. Also, the younger you are when you have a CT scan, the greater the lifetime risk of developing cancer or leukaemia.
Various studies have aimed to estimate the risk of developing cancer or leukaemia following a CT scan (see 'Further reading' below). In general, the risk is small. In many situations, the benefit of a CT scan greatly outweighs the risk.
However, as the same study concludes: ... "although clinical benefits should outweigh the small absolute risks, radiation doses from CT scans ought to be kept as low as possible and alternative procedures, which do not involve ionising radiation, should be considered if appropriate."
Because of the small risk, the Committee on Medical Aspects of Radiation in the Environment (COMARE) has recommended that routine whole-body CT scans should not be offered to people without symptoms as part of 'health checks'. They also offer various other recommendations on the use of CT scans (see 'Further reading' below).
Patient picks for Imaging

Tests and investigations
DEXA scan
DEXA scans (also called DXA scans or bone density scans) are used to check the density of bones. This test uses X-rays to show how strong bones are. A DEXA scan is different from a bone scan, which used radioactive chemicals to create a picture of the bones.
by Dr Colin Tidy, MRCGP

Tests and investigations
Hysterosalpingography
Hysterosalpingography (HSG) is a particular type of imaging of the uterus (womb) and the Fallopian tubes. It uses a dye to be able to visualise the size and shape of the uterus and check whether the Fallopian tubes are blocked.
by Dr Philippa Vincent, MRCGP
Further reading and references
- Pearce MS, Salotti JA, Little MP, et al; Radiation exposure from CT scans in childhood and subsequent risk of leukaemia and brain tumours: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2012 Jun 7.
- Hendee WR, O'Connor MK; Radiation risks of medical imaging: separating fact from fantasy. Radiology. 2012 Aug;264(2):312-21. doi: 10.1148/radiol.12112678.
- Committee on Medical Aspects of Radiation in the Environment (COMARE)
- Meer AB, Basu PA, Baker LC, et al; Exposure to ionizing radiation and estimate of secondary cancers in the era of high-speed CT scanning: projections from the Medicare population. J Am Coll Radiol. 2012 Apr;9(4):245-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jacr.2011.12.007.
- Konda SR, Goch AM, Haglin J, et al; Ultralow-Dose CT (REDUCTION Protocol) for Extremity Fracture Evaluation Is as Safe and Effective as Conventional CT: An Evaluation of Quality Outcomes. J Orthop Trauma. 2018 May;32(5):216-222. doi: 10.1097/BOT.0000000000001137.
- Singh V, Sandean DP; CT Patient Safety And Care
- Cova MA, Stacul F, Quaranta R, et al; Radiological contrast media in the breastfeeding woman: a position paper of the Italian Society of Radiology (SIRM), the Italian Society of Paediatrics (SIP), the Italian Society of Neonatology (SIN) and the Task Force on Breastfeeding, Ministry of Health, Italy. Eur Radiol. 2014 Aug;24(8):2012-22. doi: 10.1007/s00330-014-3198-6. Epub 2014 May 17.
Continue reading below
Article history
The information on this page is written and peer reviewed by qualified clinicians.
Next review due: 12 May 2028
20 Jun 2023 | Latest version

Ask, share, connect.
Browse discussions, ask questions, and share experiences across hundreds of health topics.

Feeling unwell?
Assess your symptoms online for free
Sign up to the Patient newsletter
Your weekly dose of clear, trustworthy health advice - written to help you feel informed, confident and in control.
By subscribing you accept our Privacy Policy. You can unsubscribe at any time. We never sell your data.