Balanitis
Peer reviewed by Dr Toni Hazell, MRCGPLast updated by Dr Rosalyn Adleman, MRCGPLast updated 5 Aug 2024
Meets Patient’s editorial guidelines
- DownloadDownload
- Share
- Language
- Discussion
- Audio Version
In this series:Penis problems, itchy penis, and penis painPremature ejaculationPeyronie's diseasePenile cancerCircumcisionPhimosis and paraphimosis
Balanitis is when the head of the penis becomes inflamed, causing redness, soreness, or irritation under the foreskin. It is more common in men who are uncircumcised and can be linked to hygiene issues, infections, or skin irritation. Most cases improve with simple treatment, however, recurring or severe balanitis may need medical care or lifestyle changes. This leaflet explains the common causes, symptoms, treatments, and how to reduce the risk of balanitis.
In this article:
Video picks for Men's sexual health
Key points
Balanitis is inflammation of the head of the penis (glans), often causing redness, swelling, itching, or soreness. It is common and can happen at any age.
Common causes include poor hygiene, fungal or bacterial infections, allergies, or skin conditions.
Treatment depends on the cause and may involve antifungal or antibiotic creams, steroid creams for inflammation, and improved hygiene.
Prevention includes gently cleaning the head of the penis with water, avoiding harsh soaps, and drying thoroughly.
What is balanitis?
Continue reading below
Balanitis symptoms
The most common symptoms of balanitis include redness, irritation and soreness of the head of the penis (the glans of the penis). It can range from a small patch of redness confined to part of the skin surface of the glans, to the whole glans becoming red, swollen and painful. Sometimes there is a thick clumpy discharge which comes from under the foreskin. There may be an itchy penile head.
It may be impossible to pull the foreskin back, although it is normal to have a tight foreskin in younger boys. You may also have pain or discomfort when passing urine.
Balanitis
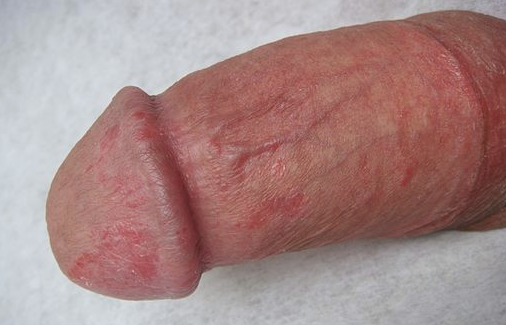
By Pal1135 (Own work) assumed [based on copyright claims] via Wikimedia Commons
What causes balanitis?
Back to contentsThere are many different causes of balanitis. These include infectious and non-infectious causes.
Poor hygiene
Poor hygiene around this area, combined with a tight foreskin, can lead to irritation by smegma. Smegma is a cheesy-like substance which forms under the foreskin if the end of the penis (the glans) under the foreskin is not cleaned. This is the most common cause of balanitis.
Infection - not sexually transmitted
Various germs (bacteria) that live on the skin in small numbers may multiply and cause infection. A common cause of balanitis is a yeast infection caused by a fungus called candida. Candida is the same germ that causes vaginal thrush in women.
Small numbers of candida commonly live on the skin and can sometimes cause infection. Some types of bacteria are also a common cause of balanitis. Any man or boy can develop an infection. However, an infection of the glans is more likely to develop if you:
Already have some inflammation of the penis due to an allergy or irritant (see below).
Have diabetes. In particular, if your diabetes is not well controlled (your blood sugar is too high) and the urine contains sugar. After going to the toilet, drops of urine which contain sugar may remain behind the foreskin and allow germs to multiply easily.
Have a phimosis. This is a condition where the foreskin does not pull back (retract) over the glans. This is common in young boys. After the age of 5 years the foreskin will usually retract easily so the glans can be gently cleaned. You are more likely to develop a balanitis if you have a phimosis, as sweat, debris and urine may collect under the foreskin. This can irritate directly, or can encourage bacteria to thrive and cause foreskin infection.
Infection - sexually transmitted
Some sexually transmitted infections (STIs) can occasionally cause balanitis. In particular, an STI is more likely if you also have inflammation of the tube (urethra) that passes out urine (a condition called urethritis).
Various STIs can cause a urethritis and a balanitis - for example, genital herpes, chlamydia, and gonorrhoea. Symptoms of urethritis include:
Pain when you pass urine.
A discharge that comes from the urethra.
Allergic reaction and irritants
The skin of the glans is sensitive. It may 'react' and become inflamed if it comes into contact with various chemicals or other substances. For example:
If you do not wash under your foreskin, old skin, urine, sweat and other debris can collect there. This may irritate the glans and may lead to inflammation.
Certain soaps and disinfectants that you may use to clean the penis.
Over-washing or scrubbing may also irritate the delicate skin of the glans.
Latex condoms, spermicides, lubricants used when having sex and the lubricant in condoms can all irritate the glans.
Chemicals spilt on your hands may be transferred to the penis when you go to the toilet.
Some washing powders or fabric conditioners that are not rinsed well from underpants.
Skin conditions
Certain skin conditions may cause a balanitis, or be mistaken for a balanitis - for example, psoriasis and some uncommon skin conditions can affect the penis. Very occasionally, an early type of skin cancer can present as inflammation of the end of the penis. It's worth getting these symptoms checked out.
Zoon's Balanitis
This affects middle-aged and older men, usually if they are not circumcised. The foreskin does not function properly and dead skin cells, urine, soap particles and other debris are trapped under the foreskin. This leads to irritation of the foreskin and the head of the penis under it. It is not caused by a penis infection. It is sometimes a sign of an underlying skin infection such as lichen sclerosus or lichen planus. It may cause an itchy penile head or a sore penile head.
Continue reading below
How is balanitis diagnosed?
Back to contentsA doctor can easily diagnose balanitis by the red and inflamed look of the end of the penis (the glans). In some cases the likely cause can be determined by the look of the inflammation. For example, the inflammation caused by candida balanitis often looks quite typical.
So, in certain cases your doctor is able to diagnose the cause and advise on treatment straightaway. If your doctor is not sure about the cause, or the balanitis does not clear with treatment, one or more of the following tests may be suggested:
Taking a sample with a small ball of cotton wool on the end of a thin stick (a swab). The sample is used to look for certain germs (bacteria) that can cause infection.
A test to check for diabetes if this is suspected.
Referral to a genitourinary medicine (GUM) clinic if an STI is a suspected cause.
Referral to a skin specialist if a skin condition or allergy is thought to be the cause. Allergy testing may be advised if an allergy is suspected.
Rarely, if the inflammation persists, removing a small sample of the inflamed skin tissue (a biopsy) may be suggested. This would be done by a skin specialist. The sample can be taken to be looked at under the microscope. This can help to find the cause.
Balanitis treatment
Back to contentsHow can you cure balanitis?
The following is recommended if you have balanitis, regardless of the cause:
Avoid soaps when inflammation is present. You can use a moisturising cream or ointment (an emollient) to clean instead of soap.
Use lukewarm water to clean your penis and then dry gently.
Some people find that salt baths are soothing whilst treatment takes effect.
If the balanitis is mild, this might be enough to allow it to clear up.
The treatment depends on the cause of the balanitis. The doctor will often prescribe:
An anti-fungal cream or a course of anti-yeast tablets is a common balanitis treatment if it is caused by candida. Anti-fungal cream can also be bought in a pharmacy.
Antibiotics will clear infection caused by germs (bacteria), including certain STIs.
A mild steroid cream to reduce inflammation is useful for balanitis caused by allergies or irritants. Sometimes a steroid cream is used in addition to anti-yeast or antibiotic medication to reduce inflammation caused by infection. (Note: if there is infection of the end of the penis (the glans) then a steroid cream should not be used alone, as steroids can make infection worse.)
It is unusual for a child to have recurring balanitis. Your GP may ask a specialist to advise. If you are an adult with a recurring problem and have a condition where the foreskin does not pull back (retract) over the glans (a phimosis), an option is to be circumcised to remove the foreskin.
Continue reading below
Can balanitis be prevented?
Back to contentsTips which may help to prevent balanitis in some cases include:
Wash the end of the penis (the glans) each day. Pull the foreskin back gently whilst in the bath or shower. Then gently clean the glans using just water, or water and a bland soap. Make sure the penis including the glans is clean and dry before you put on underpants.
If symptoms are related to condom use, try using a condom which is designed for sensitive skin.
Wash your hands before going to the toilet if you work with chemicals which can irritate delicate skin.
Use a condom each and every time you have sex with a new sexual partner.
Frequently Asked Questions
Back to contentsHow long does balanitis last?
Balanitis usually lasts up to two weeks from starting treatment. It may be better after a few days but it is important to complete the full course of treatment recommended by your doctor.
How to tell if balanitis is fungal or bacterial?
If balanitis is caused by an infection, your doctor will often be able to tell from the appearance whether it is caused by a fungus (usually candida) or bacteria. Sometimes a swab is taken and sent to a lab to confirm what type of infection there is.
Is balanitis dangerous?
Balanitis is not usually dangerous, however, if it is left untreated it can cause complications such as a spreading infection or scarring of the penis.
Does balanitis go away on its own?
Mild balanitis may go away on its own. The penis should be carefully washed and dried and you should avoid any irritants. If it does not start to get better within a few days it is important to see a doctor.
Can you have sex with balanitis?
You should avoid having sex with balanitis if it is caused by an infection or if you do not know the cause. You should wait until the infection has been treated and cleared before having sex.
Patient picks for Men's sexual health
Sexual health
Low testosterone
Low testosterone in men (testosterone deficiency) is often part of the ageing process and therefore common in older men. It can also occur at any age as a result of conditions affecting the testicles or the pituitary gland in the brain. Low testosterone can be treated with testosterone replacement therapy. Any underlying cause for the testosterone deficiency will also need treatment. The outlook will depend on the underlying cause.
by Dr Philippa Vincent, MRCGP

Sexual health
Premature ejaculation
Premature ejaculation (PE) is the term used when a man comes (ejaculates) more quickly than he and/or his partner would like. It means you ejaculate very soon after putting your penis inside (penetrating) your partner, or even before penetration. It is not really known what causes premature ejaculation. Men with premature ejaculation should not be embarrassed about discussing it with their doctor, as it can be helped by a variety of means. Many men do not seek help from their doctor for this problem so it is not known how common it is. Some studies suggest it can be as common as thirty in a hundred men. There are tablets which may be helpful, either taken regularly or as needed. Creams or sprays that numb the penis may also be used. Other treatments include certain techniques used during sex, and psychological treatments.
by Dr Hayley Willacy, FRCGP
Further reading and references
- Balanitis; NICE CKS, May 2024 (UK access only)
- Lam K, Cook DK; Chronic balanitis: When should we be concerned? Aust J Gen Pract. 2020 Dec;49(12):839-841. doi: 10.31128/AJGP-03-20-5283.
- Wray AA, Velasquez J, Khetarpal S; Balanitis. StatPearls, Jan 2024.
Continue reading below
Article history
The information on this page is written and peer reviewed by qualified clinicians.
Next review due: 4 Aug 2027
5 Aug 2024 | Latest version

Ask, share, connect.
Browse discussions, ask questions, and share experiences across hundreds of health topics.

Feeling unwell?
Assess your symptoms online for free
Sign up to the Patient newsletter
Your weekly dose of clear, trustworthy health advice - written to help you feel informed, confident and in control.
By subscribing you accept our Privacy Policy. You can unsubscribe at any time. We never sell your data.