Costochondritis
Peer reviewed by Dr Toni Hazell, MRCGPLast updated by Dr Surangi Mendis, MRCGPLast updated 5 Aug 2024
Meets Patient’s editorial guidelines
- DownloadDownload
- Share
- Language
- Discussion
In this series:Chest painBornholm diseasePleurisyPneumothorax
Costochondritis is a painful chest wall condition, caused by localised inflammation in the joints of the rib cage.
In this article:
Video picks for Chest pain
What is costochondritis?
Costochondritis is a condition of the chest wall that causes pain. People who get chest pain are often frightened they have a heart or lung problem. Fortunately, if the pain is due to costochondritis, there is no need to panic as it is not a life-threatening condition. Costochondritis usually gets better on its own with time.
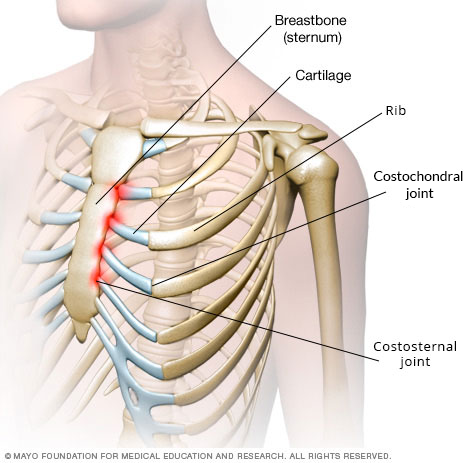
The pain of costochondritis comes from the protective ribcage, and not from the heart or lungs or blood vessels inside your chest. More specifically, it comes from one or more of the joints between your ribs and your breastbone (sternum). These joints become inflamed if you have costochondritis.
How does the chest wall work?
Back to contentsCostochondritis
'Used with permission of Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. All rights reserved.'
To understand costochondritis, you need to know a bit about the way the rib cage is put together. The rib cage is a bony structure that protects the lungs. Bones are hard and solid and they can't bend or move much. Your lungs, however, need to move, so that you can breathe.
When you take a deep breath in, your rib cage expands (try it! You will feel and see your rib cage moving). In order for the ribs to expand, they need something to allow movement. Cartilage allows this. Cartilage is a softer, flexible (but very strong) material found in joints around the body.
Cartilages attach the ribs to the breastbone (sternum) and the breastbone to the collarbones (clavicles). The joints between the ribs and the cartilages are called the costochondral joints. Those between the cartilages and the breastbone are called costosternal joints. Those between the breastbone and the collarbones are called the sternoclavicular joints.
The prefix 'costo' simply means related to the ribs. 'Chondr-' means related to the cartilage and '-itis' means inflammation. So, in costochondritis, there is inflammation in either the costochondral, costosternal or sternoclavicular joints (or a combination). This causes pain, which tends to be worse when you move, or when you press down on the affected part.
Continue reading below
Costochondritis symptoms
Back to contentsChest pain, felt at the front of the chest.
Typically, it is sharp and stabbing in nature and can be quite severe.
The pain is worse with movement and deep breathing.
Pressure over the affected area can also cause sharp pain.
Some people may feel an aching pain.
The pain is usually confined (localised) to a small area but it can spread (radiate) to a wider area.
The pain tends to wax and wane. It can settle with a change of position and quiet, shallow breathing.
The most common sites of pain are close to the breastbone (sternum), at the level of the 4th, 5th and 6th ribs.
Note: without tenderness (pain when the chest is pressed), the cause of the chest pain is unlikely to be costochondritis. Remember to seek medical advice if you are unsure of the cause of your symptoms (see the section on 'when to see a doctor').
Tietze's syndrome causes similar symptoms to costochondritis. However, it also tends to cause swelling at certain tender points on your chest wall. If you have costochondritis, there is nothing to actually see.
Bornholm disease is another similar condition but it often leads to muscle aches and pains, as well as chest pain. See the separate leaflet called Bornholm disease for more details.
How common is costochondritis?
Back to contentsIt is hard to be sure exactly how common costochondritis is, as lots of people probably have it but don't see a doctor. It seems to be quite common. Of people with chest pain who see their GP, about 1 in 5 have a cause related to the muscles, ribs and joints in their chest wall.
Continue reading below
Costochondritis causes
Back to contentsThe basic problem is inflammation but the cause of this is unknown for most people. There are some situations that are associated with inflammation and they include:
Chest infections of varying types.
Large physical exertion, like lifting heavy objects or repeated bouts of coughing.
Accidents involving the chest, like falls or car accidents.
Some types of arthritis.
Who develops costochondritis?
Back to contentsThere is no particular person more at risk of costochondritis than any other. It does tend to affect younger people, especially teenagers and young adults. It can affect children. People performing repetitive movements that strain the chest wall, particularly if they are not used to it might be more at risk of getting this condition. Some studies suggest women tend to be affected more commonly than men.
People with fibromyalgia tend to develop costochondritis more often than others. Fibromyalgia is a long-term (chronic) condition that causes widespread body pain and fatigue. See the separate leaflet called Fibromyalgia for more details.
When should I contact a doctor?
Back to contentsIt can be very difficult to know if your pain is due to costochondritis or whether - and how urgently - to see a doctor. With chest pain, it makes sense to err on the side of caution if you are unsure.
If you feel unwell, breathless, dizzy, or sweaty, or if your chest pain is very severe or spreading to your jaw or left arm then treat it as an emergency. Call 999/112/911 for an emergency ambulance
.
It is more likely that you have costochondritis if:
You are young and otherwise healthy.
You feel generally well in yourself and have no other symptoms.
You have pain which is worse when you move your chest wall or press on it.
The pain is relieved with simple painkillers such as paracetamol or ibuprofen.
If you have other symptoms in addition to the pain then consult a doctor. This would include if you have:
A cough.
Difficulty breathing.
Blood in the mucus you cough up (sputum).
Pain which spreads to other parts of the body.
A rash.
A feeling of having a 'thumping heart' (palpitations).
Also consult your doctor if the pain gets worse as you exert yourself (for example, on walking up a hill) rather than as you twist your chest around. Pain on exertion is more likely to be due to angina.
There is no specific test for costochondritis, but you might be offered other tests to rule out other causes of chest pain.
Costochondritis treatment
Back to contentsTreatment options for costochondritis include:
No treatment. Sometimes it helps just to be reassured there is no serious cause for the chest pain.
Relaxation techniques. Worry can make the pain worse. (Indeed, anxiety is a common cause of chest pain.)
Simple painkillers such as paracetamol or ibuprofen.
Injections of steroids or local anaesthetic medicines if pain is severe and other treatments have not worked.
Non-medicinal measures can be tried for relief of pain in costochondritis. Examples of such techniques include:
Heat pads.
Ice application.
Acupuncture.
Gentle stretching exercises.
Avoidance of sports or activities that worsen the pain.
Physiotherapy or chiropractic therapy to help loosen up the rib cage.
With or without treatment, most people with costochondritis get better gradually over time.
In extreme cases, an intercostal nerve block can be performed (usually by a doctor specialising in pain and/or anaesthetics). This involves injection of a local anaesthetic medicine around the painful ribs.
This blocks the nearby intercostal nerve and temporarily disrupts nerve impulses to stop the pain. Nerve blocks can last several weeks or months. In repeated, severe cases of costochondritis, a series of these injections can be given to permanently calm the nerve causing the pain.
What is the outlook?
Back to contentsThe outlook (prognosis) for costochondritis is generally very good. Most cases of costochondritis are mild and settle reasonably quickly. This happens with or without simple medications.
How long does costochondritis last for?
9 out of 10 people with costochondritis are pain-free after three weeks. In nearly all cases, the condition has completely gone within a year. Occasionally, if you are unlucky, it lasts longer. Costochondritis may return; however, this is unlikely.
Patient picks for Chest pain

Chest and lungs
Pneumothorax
A pneumothorax is sometimes called a "collapsed lung" and it describes the condition in which air has become trapped next to a lung. Many cases occur without warning, particularly in healthy young men. Some develop as a complication of a chest injury or a lung disease. The most common symptom is a sudden sharp chest pain followed by pains on breathing in. Some people become breathless. In most cases, the pneumothorax clears without needing treatment. The trapped air of a large pneumothorax may need to be removed if it causes breathing difficulty. An operation is needed in some cases.
by Dr Philippa Vincent, MRCGP

Chest and lungs
Pleurisy
Pleurisy is due to inflammation of the pleura next to the lung. It is most often caused by infection with a germ (a viral infection). In these cases the pain can be severe but soon goes. Various other lung disorders can also cause a 'pleuritic pain' similar to pleurisy. A pleuritic pain is a chest pain which is typically sharp and 'stabbing' in a part of the chest. The pain is usually made worse when you breathe in or cough.
by Dr Doug McKechnie, MRCGP
Further reading and references
- Schumann JA, Sood T, Parente JJ; Costochondritis
- Rokicki W, Rokicki M, Rydel M; What do we know about Tietze's syndrome? Kardiochir Torakochirurgia Pol. 2018 Sep;15(3):180-182. doi: 10.5114/kitp.2018.78443. Epub 2018 Sep 24.
- Mott T, Jones G, Roman K; Costochondritis: Rapid Evidence Review. Am Fam Physician. 2021 Jul 1;104(1):73-78.
- de Carvalho JF; Tietze's Syndrome. Mediterr J Rheumatol. 2022 Dec 31;33(4):467-468. doi: 10.31138/mjr.33.4.467. eCollection 2022 Dec.
Continue reading below
Article history
The information on this page is written and peer reviewed by qualified clinicians.
Next review due: 4 Aug 2027
5 Aug 2024 | Latest version
27 Jan 2011 | Originally published
Authored by:
Dr Katrina Ford, MRCGP

Ask, share, connect.
Browse discussions, ask questions, and share experiences across hundreds of health topics.

Feeling unwell?
Assess your symptoms online for free
Sign up to the Patient newsletter
Your weekly dose of clear, trustworthy health advice - written to help you feel informed, confident and in control.
By subscribing you accept our Privacy Policy. You can unsubscribe at any time. We never sell your data.