Right upper quadrant pain
Peer reviewed by Dr Rachel Hudson, MRCGPLast updated by Dr Caroline Wiggins, MRCGP Last updated 16 Dec 2024
Meets Patient’s editorial guidelines
- DownloadDownload
- Share
- Language
- Discussion
- Audio Version
This leaflet looks at pains which can develop in the upper part of the tummy (abdomen/abdominal cavity) on your right-hand side. It deals with possible causes, how a diagnosis might be made and what the treatment might be.
In this article:
Video picks for Abdominal pain
Continue reading below
Where is my right upper quadrant?
The right upper quadrant (RUQ) is a section of your tummy (abdomen). Look down at your tummy, and mentally divide the area from the bottom of your ribs down to your pubic hair into four quarters. The quarter on your right side closest to your ribs is your RUQ.
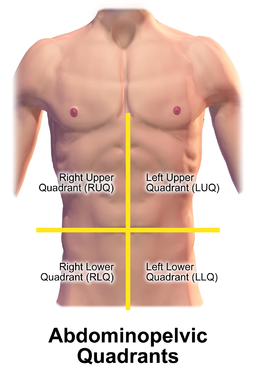
© By Blausen.com staff (2014). “Medical gallery of Blausen Medical 2014”. WikiJournal of Medicine 1 (2). DOI:10.15347/wjm/2014.010. ISSN 2002-4436
By Blausen.com staff (2014). “Medical gallery of Blausen Medical 2014”. WikiJournal of Medicine 1 (2). DOI:10.15347/wjm/2014.010. ISSN 2002-4436
Which organs are in my right upper quadrant?
Back to contentsAbdominal Quadrant Regions
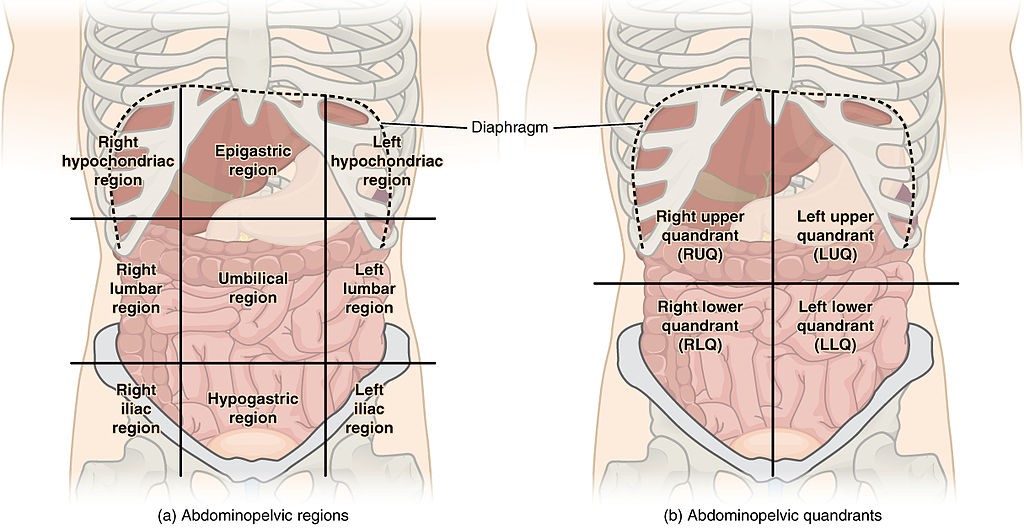
© OpenStax, CC BY 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
OpenStax, CC BY 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
The organs within your right upper quadrant are your:
Liver.
Gallbladder.
Duodenum and some other parts of your large and small bowel.
Right kidney (at the back behind the other organs).
Part of the pancreas.
The aorta.
There are also the skin and nerves of that section.
Continue reading below
What causes right upper quadrant pain?
Back to contentsPain can come from any of the organs mentioned above, and these are the source for the most common causes. But the human body is never simple, so pain can also come from other areas of your body. This is called 'referred' pain. So this widens the possible causes of pain.
In adults, the most common causes of right upper quadrant pain are:
Less common causes are discussed later in this leaflet.
Gallstones and gallbladder problems
Gallstones don't necessarily cause any symptoms but if they get stuck in the bile duct they can cause pain. This is called biliary colic and is typically a severe cramp-like pain in the RUQ shortly after eating a fatty meal. An infection may follow, called cholecystitis, which will give you a more persistent pain in the RUQ, with a high temperature.
See the separate leaflets called Gallstones and bile and Cholecystitis for more information.
Kidney stones and infections
Problems with the kidney tend to give you pain more around the right-hand side of the right upper quadrant, or in your back (loin), but the pain may spread and involve the front of the tummy (abdominal) area. Kidney stones can cause a severe pain (usually round the back) which occurs in spasms lasting from a few minutes to several hours.
There may also be blood in your wee. A kidney stone or infection can cause pain anywhere along your urinary tract. So this could be anywhere from the loin in your back, around to the front, the RUQ, or down to the lower part of your tummy. It may be associated with a fever, pain when you wee, or going to the loo more frequently.
See the separate leaflets called kidney infection (Pyelonephritis) and Kidney stones for more information.
Shingles
Commonly, people notice pain from shingles before the rash appears. The pain tends to be quite sharp or burning, and you may feel not quite right in yourself. A few days later a blistery rash appears. The RUQ is a common place for a shingles rash.
Other people find they continue to get a pain long after the rash of shingles has gone. This is called postherpetic neuralgia.
See the separate leaflet called Shingles (Herpes Zoster) for more information.
Liver problems
The liver takes up a large part of your right upper quadrant but, in fact, it doesn't very often give you pain. Causes of pain from the liver include:
Infection causing inflammation of the liver (hepatitis). This will usually result in jaundice and a fever and feeling generally unwell in addition to some pain in that area. Pain is not necessarily a feature. There are a number of types of hepatitis, including hepatitis A, hepatitis B and hepatitis C.
Abscess. This is a collection of pus causing pain, tenderness and fever.
Alcoholic liver disease. Too much alcohol can damage your liver, which may affect its function, turn your skin yellow (jaundice) and give you RUQ pain.
Liver cancer - this can start in the liver or have spread from other cancers. Primary cancer in the liver is unusual. The liver may enlarge in certain blood cancers, such as lymphomas or leukaemias, causing discomfort.
Gut problems
Several problems in your gut can give you pain in the right upper quadrant. For example:
Duodenal ulcer. Pain typically comes on a couple of hours after eating and may be improved by taking antacids. The level of pain can gradually build up over time, eventually becoming severe and may be associated with bringing up (vomiting) blood. This is an emergency and you should call an ambulance to go directly to hospital if this occurs. See the separate leaflet called Duodenal ulcer for more information.
Gastroenteritis. Infections in your gut tend to give you pain all over your tummy, or more in the middle; however, occasionally the pain may be in the RUQ area. It is usually associated with diarrhoea and/or being sick (vomiting). You may have a mild fever. See the separate leaflet called Gastroenteritis for more information.
Indigestion (dyspepsia) can give you a pain in the upper part of your tummy, along with bloating and acid reflux. See the separate leaflet called Indigestion (Dyspepsia) for more information.
Long-term conditions such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis can give rise to pain anywhere in the tummy. They usually cause loose stools, sometimes with blood. See the separate leaflets called Crohn's disease and Ulcerative colitis for more information.
Irritation of the diaphragm. The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle at the bottom of the ribs. Pain can be caused by various conditions in this way. This includes a ruptured ectopic pregnancy, pneumonia, or a hernia involving the diaphragm.
Pain coming from the pancreas
Your pancreas is in the middle of the upper part of your tummy. Chemicals (enzymes) made by cells in the pancreas pass into the guts to help digest food. The hormones insulin and glucagon are also made in the pancreas and help to regulate the blood sugar level.
It can become inflamed in the conditions acute pancreatitis and chronic pancreatitis, causing upper tummy pain, usually with feeling sick (nausea) and/or being sick (vomiting). The pain is usually in the centre of the upper part of your tummy, but can be felt on the right. In acute pancreatitis there is usually also a fever and you may feel very unwell in yourself.
Cancers of the pancreas can also cause upper tummy pain although they can cause pain elsewhere such as the back, and, unfortunately, they often don't cause any symptoms until the person is very unwell with advanced cancer.
Pain coming from the aorta
Your aorta is the main blood vessel of your body, carrying blood from your heart, and passing down the middle of your tummy, taking blood down to your legs and elsewhere. In some people this can swell, making it more vulnerable to leaking or bursting. This is called an aortic aneurysm.
If it develops a leak, you can get a tummy pain which you may also feel in your back. Rarely, the aorta can develop a tear in a weakened area of the lining of the aorta. This is called an aortic dissection. If the aorta bursts (ruptures), you will get a very severe pain in your tummy, back or chest and feel very unwell indeed. Any pain which is suspected to come from the aorta is a medical emergency and needs immediate treatment.
What causes right upper quadrant pain in pregnancy?
Any of the above conditions can cause pain in the right upper quadrant whether you are pregnant or not, so you should always be checked out. In early pregnancy it is important to consider ectopic pregnancy. However, in pregnancy a common cause of discomfort is the pressure of the womb pressing on other organs, and pressing them into the diaphragm.
Also, problems with indigestion tend to be common in pregnancy, again at least partly due to the pressure on the stomach. Urinary tract infections are also more common in pregnancy.
What causes right upper quadrant pain in children?
Back to contentsIn young children it is often quite difficult for them to show exactly where the pain is. If this is the case, the range of options widens to almost any cause of tummy ache. In children common causes include:
Mesenteric adenitis. In children with infections such as colds, glands within the tummy commonly become inflamed giving them tummy ache.
Appendicitis. Usually this gives pain in the lower right part of the tummy. However, often the pain of appendicitis starts in the middle of the tummy, around the tummy button. And if a child can't show you exactly where the pain is, or if the appendix has burst (ruptured), appendicitis may be a possible diagnosis to consider.
Pneumonia. Infections of the lower parts of the lungs may cause pain in the tummy area.
Continue reading below
What are the other possible causes?
Back to contentsAs well as the more common causes already described, there are many other conditions which occasionally cause right upper quadrant pain.
These include:
Heart attack (myocardial infarction). Heart attacks normally present with chest pain, radiating to the left arm or neck, or a tightness in the chest. Occasionally they can cause pain in the RUQ. Usually you would feel unwell in yourself if you were having a heart attack - for example, feel sweaty or breathless.
Pneumonia. This is an infection in the lung and normally gives you cough, and a high temperature (fever), with or without breathlessness and pain in your chest. However, if the infection is in the lower part of your right lung, you may feel the pain in your RUQ. Other types of chest infections such as pleurisy can also sometimes give you a pain so low in your chest that it feels as if it is in your tummy (abdomen).
Problems with the pancreas. This includes pancreatitis and cancer of the pancreas. Usually problems with the pancreas give you pain more in the middle of your upper tummy, which may also be felt in your back between your shoulder blades. But occasionally it can cause a pain on the right side.
A serious complication of type 1 diabetes, called diabetic ketoacidosis. This makes you very unwell generally, but occasionally tummy pain can be one of the symptoms.
In a condition called Addison's disease, a complication called an Addisonian crisis occasionally can give you tummy pain. Again you would be unwell in other ways other than the pain.
Rare complications of pregnancy affecting the liver.
Pain which is referred from problems in the pelvis, which is below the tummy. This might include conditions such as infections (pelvic inflammatory disease) or ovarian cysts. Again the pain in the RUQ would usually be accompanied by one or more typical symptoms of these conditions.
Budd-Chiari syndrome is a rare condition where the veins in the liver become blocked.
These listed causes are not exhaustive, and many other conditions occasionally cause pain in the right upper quadrant.
Should I see a doctor for upper right abdominal pain?
Back to contentsYes, if you have a pain which doesn't settle, you will probably need to see a health professional to help work out the cause. See a doctor urgently if:
Your skin has turned yellow (this is called jaundice).
Your wee has gone darker and your poo lighter (this suggests a blockage in the tubes around your liver and gallbladder).
Your pain is very severe.
You have recently lost weight without trying.
You are bringing up (vomiting) blood, or have blood in your poo (including a very dark coloured poo which can be caused by old blood from high up in the gut).
You have a high temperature with shaking (rigors).
You feel short of breath.
How is right upper quadrant pain diagnosed?
Back to contentsThe doctor will be able to get a reasonable idea of the cause for the pain by asking you some questions and physically examining you. They may be able to find the cause simply from doing so. For example, if they find the typical rash of shingles, you will need no further tests to find the cause.
If examination is normal, that already rules out quite a few possible diagnoses. The doctor will certainly need to feel your tummy (abdomen) in the area you have the pain, but may also need to examine other parts too, such as the rest of your tummy and your chest.
Are tests needed?
You may be asked to provide a sample of urine, to check the colour and to rule out kidney problems. You may need further tests, depending on what they think is causing the pain.
Possible tests might include blood tests to check the function of your liver, rule out any inflammation or infection in your system, an ultrasound scan to look for common conditions such as gallstones, or a look into your stomach and upper bowel with a camera (endoscopy) and other scans and 'scopes'.
What are the next steps?
Back to contentsThis depends on what has been discovered so far through the tests above. More specific tests may be needed depending on where it is thought the pain is coming from. If your pain is thought to be coming from your guts, you are likely to have some type of endoscopy, which is an examination of the inside of your guts with a camera.
A more specific type called endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) can examine the tubes around your gallbladder and pancreas. In some cases special radio-isotope scans may be used. These show up certain organs and tissues by using a small dose of a radioactive chemical.
If you might have a kidney problem, you might have a specialised form of computerised tomography (CT) scan, with a dye injected to highlight your urinary tract.
A chest X-ray might be needed to rule out a problem in your lungs, such as infection.
It is very unlikely that you would need ALL these tests. You are likely to need a few tests only. For example, if gallstones are found on the ultrasound scan, you would need no other tests.
What if no cause is found after tests?
Back to contentsObviously if any serious cause has been ruled out, this is a relief, but doesn't settle the pain. There are so many possible causes that multiple tests may be needed for your doctor to be sure that they have ruled out all serious causes.
Treatment for right upper quadrant pain
Back to contentsThere is no single answer to this until you know what the cause of your pain is. See the relevant leaflet for the condition you are diagnosed with. Treatments for a few of the common causes of right upper quadrant pain are briefly discussed below.
Gallstones. In some cases symptoms are not very troublesome and can be managed by sticking to a low-fat diet only. Many people choose to have their gallbladder removed, in an operation called a cholecystectomy. This can usually be done by keyhole (laparoscopic) surgery.
Cholecystitis is treated initially with antibiotics, usually in hospital via injections or a drip (intravenous antibiotics). Once the infection has been treated, a cholecystectomy is usually advised.
Shingles. The pain and rash settle on their own in time, but some people may be advised to take an antiviral tablet to help reduce the risk of long-term nerve pain after shingles.
Kidney infections are treated with antibiotics. Mild infections can be treated with antibiotics at home. If you are very unwell you may need admission to hospital for intravenous antibiotics and fluids.
Kidney stones. Small kidney stones pass on their own eventually, in which case you will need to drink plenty of fluids. Larger kidney stones may need one of a number of procedures done to break them up or remove them altogether.
A duodenal ulcer is usually treated with acid-suppressing medication, as is indigestion.
What is the outlook?
Back to contentsAgain, outlook (prognosis) depends entirely on the cause of the pain. Your doctor should be able to give you an idea of the outlook once a diagnosis has become clear.
Patient picks for Abdominal pain

Digestive health
Spleen pain
This leaflet gives a brief overview of the spleen and its functions.
by Dr Colin Tidy, MRCGP

Digestive health
Mesenteric adenitis
Mesenteric adenitis means swollen (inflamed) lymph glands in the tummy (abdomen), which causes tummy pain. It is sometimes called mesenteric lymphadenitis. The mesentery is the part of the tummy where the glands are located. Adenitis means inflamed lymph glands.
by Dr Doug McKechnie, MRCGP
Further reading and references
- Kim JS; Acute abdominal pain in children. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2013 Dec;16(4):219-24. doi: 10.5223/pghn.2013.16.4.219. Epub 2013 Dec 31.
- Cartwright SL, Knudson MP; Diagnostic imaging of acute abdominal pain in adults. Am Fam Physician. 2015 Apr 1;91(7):452-9.
- Gallstones; NICE CKS, June 2024 (UK access only)
- Cholecystitis - acute; NICE CKS, July 2021 (UK access only)
Continue reading below
Article history
The information on this page is written and peer reviewed by qualified clinicians.
Next review due: 15 Dec 2027
16 Dec 2024 | Latest version

Ask, share, connect.
Browse discussions, ask questions, and share experiences across hundreds of health topics.

Feeling unwell?
Assess your symptoms online for free
Sign up to the Patient newsletter
Your weekly dose of clear, trustworthy health advice - written to help you feel informed, confident and in control.
By subscribing you accept our Privacy Policy. You can unsubscribe at any time. We never sell your data.